What is the Customer Journey Map?

Understanding the customer journey is crucial for businesses aiming to deliver exceptional experiences and achieve long-term success. By mapping the various touchpoints and interactions a customer has with a brand, businesses can pinpoint areas for improvement, refine their marketing strategies, and ultimately foster stronger, more loyal relationships with their customers. To achieve this, learn how to create a customer journey map, identify key touchpoints and pain points, and analyze the results by reading below.
What is the Customer Journey – Definitions
The customer journey is the series of steps a customer goes through when interacting with a company. It encompasses various interactions, including discovering a product or service, researching it, making a purchase, engaging with the brand, using the product, and seeking support. The customer journey differs from the customer experience, as the customer journey describes the interactions a customer has with a company, while the customer experience is the customer’s perception of those interactions.
Customer journey map
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the customer’s experience with a company. It provides valuable insights into the needs and motivations of potential customers at each stage of their journey.
By mapping out this journey, businesses can identify areas for improvement, reduce friction along the way, and create a more helpful and enjoyable experience for their leads and customers
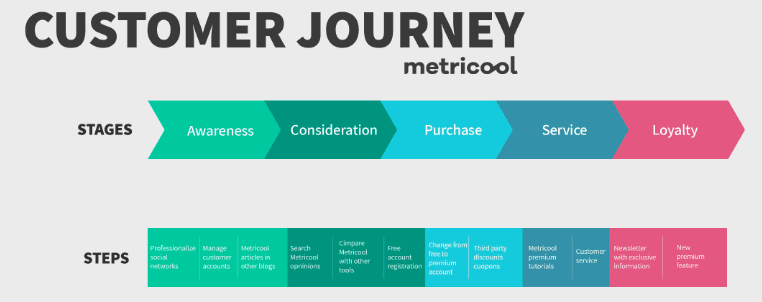
Customer journey stages
The customer journey encompasses the entire experience a customer has with a brand. It outlines the steps needed to enhance the overall customer experience and lifecycle, build loyalty, and foster long-term relationships.
The five stages of the customer journey are:
- Awareness: The potential customer becomes aware of your product or service and starts researching it.
- Consideration: Customers evaluate their options and compare different solutions.
- Purchase: The customer makes a purchase, having determined that your product or service best meets their needs.
- Service: Customers begin using the product or service they purchased and assess their satisfaction with the purchase.
- Loyalty: The customer becomes a loyal brand advocate and recommends the product or service to others.
The customer journey differs from a marketing funnel. The marketing funnel is a linear sequence divided into stages like awareness, consideration, conversion, and customer retention. It typically focuses on a shorter timeframe from initial contact to conversion. The customer journey is much more fluid and nonlinear, encompassing the entire customer lifecycle.
Customer journey touchpoints
Touchpoints are the various interactions a customer has with a company throughout their journey.
Customer touchpoints can include:
- Discovering the product
- Researching options
- Engaging with the brand on social media
- Making a purchase
- Using the product
- Seeking support
Customer journey pain points
Pain points are the challenges or obstacles customers face during their interactions with a company. These pain points can occur at any stage of the journey and negatively impact the customer experience.
Examples of customer pain points include:
- Difficulty finding information
- A confusing purchasing process
- Poor customer support
- Dissatisfaction with the product or service
Why is Defining the Customer Journey Important?
Defining the customer journey is crucial because it helps companies understand the complex process customers go through when interacting with a brand. By mapping out this journey, companies can identify areas for improvement, decrease friction along the way, and create a more helpful and delightful experience for their leads and customers.
Benefits of a customer journey map
Creating a customer journey map offers several key benefits:
- Understanding customer behavior and preferences
- Identifying effective touchpoints and optimizing them to increase sales
- Diagnosing product or service issues and addressing them promptly
- Supporting marketing efforts with targeted messaging and campaigns
- Increasing customer engagement, trust, and loyalty
- Boosting conversion rates by fixing gaps in the customer journey
How to Create a Customer Journey Map
Creating a customer journey map is a powerful tool for businesses to understand and improve the experiences they provide to their customers.
By mapping out the various interactions and touchpoints that customers have with your brand, you can identify areas for improvement and develop targeted strategies to enhance the overall customer experience.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you create a customer journey map that drives meaningful change.
1. Define your goals & decide on map type
Before you begin creating your customer journey map you need to define your goals and decide on the type of map that best fits your objectives.
Consider what you hope to accomplish through the map. Which customers are you targeting? Which types of experiences do you want your maps to highlight?
There are several types of customer journey maps. You need to choose the type of map that best fits your goals:
- Current State: Focuses on the customer’s current experience with the brand.
- Future State: Outlines the desired customer experience and the changes needed to achieve it.
- Day-in-the-Life: Examines the customer’s entire day, including interactions with the brand and other activities.
- Empathy Map: Focuses on understanding the customer’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
- Service Blueprint: Combines the customer journey with the internal processes and resources needed to deliver the service.
2. Create buyer personas / target audience
Your customer journey map should be tailored to the needs of your target audience. For this, create detailed profiles of your target customers. Conduct market research to gather data on your target audience, including demographics, psychographics, and market trends.
Consider the following for your target audience:
- Demographics: Age, gender, occupation, income, education level, and other relevant demographic information.
- Goals and Objectives: What are their goals and objectives? What do they hope to achieve?
- Pain Points: What are their pain points? What challenges do they face?
- Behaviors: What behaviors do they exhibit? How do they interact with your brand?
- Values and Motivations: What values and motivations drive their decisions?
- Personality Traits: What personality traits do they possess? Are they introverted or extroverted?
Group similar customers together based on their characteristics, needs, and behaviors. And use your buyer personas to tailor your customer journey map to their needs and pain points. Make sure that the map is relevant to your target audience by incorporating their goals, pain points, and behaviors.
3. Gather & analyze customer data
To understand the customer journey, collect both internal and external data on customer experiences.
This includes quantitative and qualitative information from various sources:
- Surveys, interviews, testimonials, reviews, and feedback from customer relations teams: Identify pain points that lead to fall-offs during the buying journey.
- Customer feedback: Ask about their experiences, such as how they found your company or what they would like to see improved. Collect feedback through social media, email, and customer support.
- Call center recordings, support logs, and other data: Understand how customers interact with your business.
Analyze the data to identify patterns and trends in customer behavior, preferences, and pain points. This will help you better understand the customer journey and identify areas for improvement.
4. Identify touchpoints and stages
Map out the various interactions customers have with your brand and the stages they go through. Ensure your map includes all touchpoints, such as online and offline interactions, to provide a comprehensive view of the customer journey.
✅ Online Touchpoints:
- Website and mobile app interactions
- Social media engagement
- Email campaigns and newsletters
- Online advertising and sponsored content
- Search engine results and search engine optimization (SEO)
✅ Offline Touchpoints:
- In-store experiences
- Customer service interactions
- Sales calls and meetings
- Trade shows and events
- Print and television advertising
5. Identify pain points & emotions
Pain points refer to the challenges, obstacles, or difficulties that customers face during their journey with your brand. Identifying these pain points and the emotions your customers face is crucial to understanding the customer experience and developing targeted strategies to improve it.
Analyze the data to identify challenges and obstacles customers face during their journey. Understand customer feelings, such as frustration or confusion, to better understand their experiences.
Some common pain points that customers may experience include:
- Difficulty Finding Information: Customers may struggle to find the information they need on your website or through customer support.
- Long Wait Times: Customers may experience long wait times for customer service or support.
- Confusing Product Options: Customers may find it difficult to navigate complex product offerings or understand the differences between products.
- Poor Communication: Customers may receive unclear or inconsistent communication from your brand.
- Technical Issues: Customers may encounter technical issues, such as website errors or app crashes, that hinder their ability to interact with your brand.
Understanding customer feelings is crucial to identifying pain points. Pay attention to emotions such as:
- Frustration: Customers may feel frustrated when they encounter difficulties or obstacles during their journey.
- Confusion: Customers may feel confused when they are unable to find the information they need or understand the product offerings.
- Disappointment: Customers may feel disappointed when their expectations are not met or when they encounter technical issues.
- Anxiety: Customers may feel anxious when they are unsure about the next steps in their journey or when they are waiting for a response from your brand.
6. Build customer journey map
Once you have identified the touchpoints, pain points, and stages, it’s time to create a visual representation of the customer journey. This will help you understand how customers interact with your brand at each stage and identify areas for improvement.
To create the map, follow these steps:
- Start with the Awareness Stage: Begin by mapping the touchpoints and stages from the Awareness Stage to the Post-Purchase Stage.
- Add Touchpoints and Stages: Add each touchpoint and stage to the map, ensuring that they are accurately represented and easy to understand.
- Highlight Pain Points: Highlight the pain points and areas of frustration that customers experience during their journey.
- Add Customer Feelings: Include customer feelings and emotions, such as frustration, confusion, or disappointment, to better understand their experiences.
7. Analyze, make changes & find solutions
Once you have created the map, analyze it to identify areas for improvement and potential solutions.
Ask yourself questions like:
- What are the most common pain points and areas of frustration?
- Where do customers tend to drop off or become frustrated?
- What are the most common complaints or criticisms customers have about our brand?
- What are the most significant opportunities for improvement?
Based on your analysis, identify areas for improvement and potential solutions. Some potential areas for improvement include:
- Streamlining Processes: Simplify or automate processes to reduce wait times and improve efficiency.
- Enhancing Communication: Improve communication by providing clear and consistent information to customers.
- Addressing Technical Issues: Fix technical issues so your website and apps are user-friendly and reliable.
- Providing Personalized Experiences: Tailor your offerings and communication to individual customers’ needs and preferences.
Prioritize the areas for improvement based on their impact on the customer experience and their potential to drive business growth. Focus on the most critical issues first and work your way down the list.
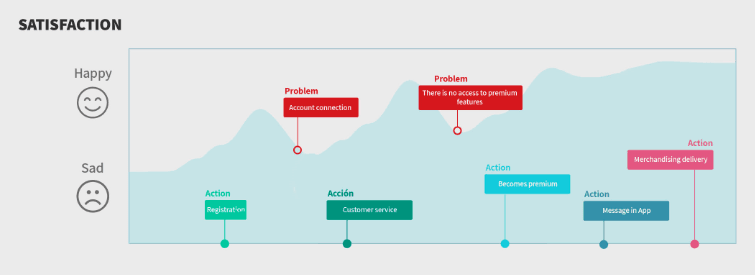
Customer Journey Map Example
Customer Journey Analytics Tools
Creating and analyzing customer journey maps can be a complex and time-consuming process. Fortunately, there are several tools available to help streamline this process and provide valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences.
Here are some popular tools that can aid in creating and optimizing customer journey maps:
- Metricool: Provides data on website traffic and social media users, helping you understand the source of traffic and engagement metrics for your brand. This tool is useful for tracking and analyzing online campaigns and their impact on customer behavior.
- Crazy Eggs: Offers website heat maps to analyze user behavior, visualizing how users interact with your website and highlighting areas of high engagement and potential areas for improvement.
- Convert Flow: Helps capture more leads through landings and websites by optimizing the conversion process through user behavior analysis and identifying pain points.
- Wickedreports: A comprehensive tool for creating and optimizing customer journey maps. It analyzes the touchpoints of your online campaigns, helping you optimize them for better results.

